renewable resource: a resource that can be replaced in a short period of time.
ozone layer: a layer of ozone gas in the atmospherre that screens out much of the Sun´s UV rays.
fossil fuel: a fuel formed from the decay of ancient forms of life.
smog: a mixture of smoke and fog.
acid rain: moisture that falls to Earth after being mixed with wastes from burned fossil fuels.
Sunday, September 26, 2010
vocabulary 15
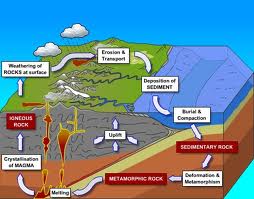
Rock: a natully formed solid in the crust,made up of ome or mlre minerals.
igneous rock: a rock formed when melted rock material cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock: a rock made of bits ofmatter joined together.
fossil: any remains or imprint of living things of the past.
metamorphic rock: a rock formed under heat and pressure from another kind of rock.
humus: decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution: adding any harmful subtances to Earth´s land,water,or air.
rock cycle: rocks changing from one form into another in a never-ending series of process.
igneous rock: a rock formed when melted rock material cools and hardens.
sedimentary rock: a rock made of bits ofmatter joined together.
fossil: any remains or imprint of living things of the past.
metamorphic rock: a rock formed under heat and pressure from another kind of rock.
humus: decayed plant or animal material in soil.
pollution: adding any harmful subtances to Earth´s land,water,or air.
rock cycle: rocks changing from one form into another in a never-ending series of process.
Saturday, September 25, 2010
vocabulary 14
mineral: a solid materialof Earth´s crust with a definite composition.
luster: the way light bounces off a mineral´s surface.
streak: the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed against a hard,rough surface.
hardness: how well a mineral resists scratching.
cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surfaces.
ore: a mineral containing a useful subtance.
gem: a mineral valued for being rare and beutiful.
nonrenewable resource: a resource that cannot be replaced within a short period of time or at all.
luster: the way light bounces off a mineral´s surface.
streak: the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed against a hard,rough surface.
hardness: how well a mineral resists scratching.
cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along flat surfaces.
ore: a mineral containing a useful subtance.
gem: a mineral valued for being rare and beutiful.
nonrenewable resource: a resource that cannot be replaced within a short period of time or at all.
vocabulary 9
kinetic energy: the energy of a moving object.
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.
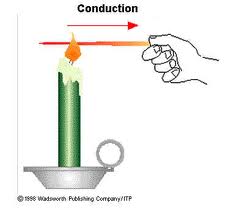
conduction: movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a cooler object;the material remains in place.
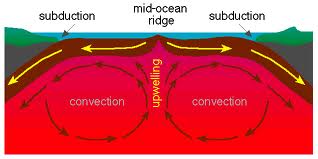
convection: movement of energy by the flow of matter from place to place.
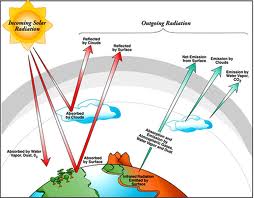
radiation: movementof energy in the form of waves that can travel trough empty space.
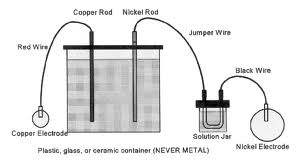
wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electric current.
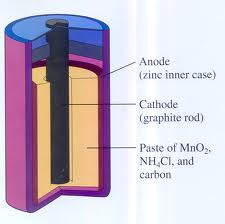
dry cell battery: a battery that uses "dry chemicals" to produce an electric current.
potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.
conduction: movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a cooler object;the material remains in place.
convection: movement of energy by the flow of matter from place to place.
radiation: movementof energy in the form of waves that can travel trough empty space.
wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electric current.
dry cell battery: a battery that uses "dry chemicals" to produce an electric current.
vocabulary 13
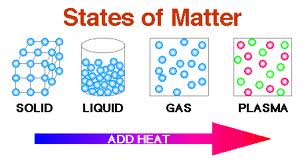
state of matter: any of the forms matter can exist in.
melting point: the temperature at which a solid changes state into a liquid.
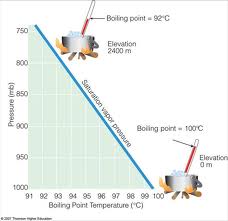
boiling point: the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a gas.
freezing point: the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a solid.
melting point: the temperature at which a solid changes state into a liquid.
boiling point: the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a gas.
freezing point: the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a solid.
vocabulary 12
opaque: completely blocking light from passing trhough.
transparent: letting all light trough,so that objects on the other side can be seen clearly.
translucent: letting only some light trough,so that objects on the other side can be seen blurry.
polarization: allowing light viobrations to pass trough in only one direction.
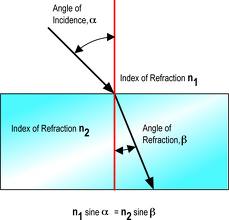
refraction: the bending of light rays as they pass from one subtance into another.
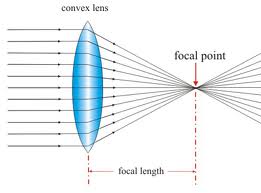
convex lens: a lens that curves outward and brings light rays together.
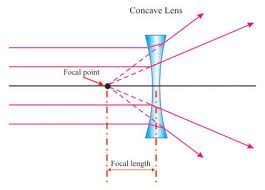
concave lens: a lens that curbves inward and spreads light rays apart.
transparent: letting all light trough,so that objects on the other side can be seen clearly.
translucent: letting only some light trough,so that objects on the other side can be seen blurry.
polarization: allowing light viobrations to pass trough in only one direction.
refraction: the bending of light rays as they pass from one subtance into another.
convex lens: a lens that curves outward and brings light rays together.
concave lens: a lens that curbves inward and spreads light rays apart.
vocabulary 11
bioluminecence: light produced by living organisms.
light ray: a straight-line beamof light as it travels outward from its source.
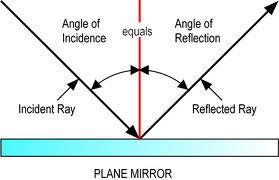
law of reflection: the angle of anincoing light ray equals the angle of the reflected ray.
concave mirror: a mirror that curves in on the shiny side.
convex mirror: a mirror that curves out on the shiny side.
light ray: a straight-line beamof light as it travels outward from its source.
law of reflection: the angle of anincoing light ray equals the angle of the reflected ray.
concave mirror: a mirror that curves in on the shiny side.
convex mirror: a mirror that curves out on the shiny side.
Tuesday, September 21, 2010
Land Pollution on street 2 San Antonio
Land Pollution is the addition of undesirable matter to the land that damage the terrestrial organisms , reduce the uses of the land by man for agricultural, residential , recreational or other purposes or increase the risk of the health hazards to man.
The description of the problem is that the people that pass cklose to my neighborhood or my house through their wastes and then all the days have bad smells , and sometimes when my neighbor don´t cut her tree ; the leaves and her wastes final in my house and is the same with the others neighbors that trough her wastes in my house.
Posible solution: My possible solution is that don´t through wastes in the neighborhood or wastes because you don´t is the person that need to clean ; and sometimes that wastes that you through can be sick sometimes and also for some animals.
Tuesday, September 7, 2010
Album #2
Introduction:
In these chapter we will learn how the force of gravity was discovered by Newton, how the sun affects the Earth, the live in it, and we will compare the difference between the moon and our beloved planet.
Planers and her describtions:
Mecury: Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in thesolar system.Mercury has no natural satellites,and its only known geologiocal features besides impact craters are lobed ridges or rupes, probably produced by a period of contraction early in itshistory.
Venus:Venus is close in zise to Earth, and like Earth, has a thick silicate mantle around an iron core, a substantial atmosphere and evidende of international geological activity. Venus has no natural satellites. It is the hottest paknet, with surface temperature.
Earth:Earth is the largest and denset of the inner planets, the only obe known to have current geological activity, and is the only place in the universe where life is known to exist. Earth´s atmosphere is radically different from those of the other planets, having been altered by the presence of life to contain 21% free oxygen . It has one natural satellite,the moon ,the only large satellite of a terrestrial planet in the Solar System.
Mars:Mars is the smaller than the Earth and Venus. It possesses an atmosphere of mostly carbon dioxide with a surface pressure.Its red colour comes from iron oxide ( rust) in its soil. Mars has two tiny natural satellites ( Deimos and Phobos) though to be captured asteroids.
Jupiter:Jupiter´s strong international heat creates a number of semi-permanent features in its atmosphere, such as cloud bands and the Great Red Spot. Jupiter has 63 known satellites.
Sturn:Saturn is distinguished by its extensive ring system, has several similarities to Jupiter, such as its atmospheric composition and magnetospere. The rings of Saturn are made up of small ice and rock particles . Saturn has 2 confirmed satellites; two which Titan and Enceladus, show signs of geological activity, though they are largely made of ice.

In these chapter we will learn how the force of gravity was discovered by Newton, how the sun affects the Earth, the live in it, and we will compare the difference between the moon and our beloved planet.
Planers and her describtions:
Mecury: Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in thesolar system.Mercury has no natural satellites,and its only known geologiocal features besides impact craters are lobed ridges or rupes, probably produced by a period of contraction early in itshistory.
Venus:Venus is close in zise to Earth, and like Earth, has a thick silicate mantle around an iron core, a substantial atmosphere and evidende of international geological activity. Venus has no natural satellites. It is the hottest paknet, with surface temperature.
Earth:Earth is the largest and denset of the inner planets, the only obe known to have current geological activity, and is the only place in the universe where life is known to exist. Earth´s atmosphere is radically different from those of the other planets, having been altered by the presence of life to contain 21% free oxygen . It has one natural satellite,the moon ,the only large satellite of a terrestrial planet in the Solar System.
Mars:Mars is the smaller than the Earth and Venus. It possesses an atmosphere of mostly carbon dioxide with a surface pressure.Its red colour comes from iron oxide ( rust) in its soil. Mars has two tiny natural satellites ( Deimos and Phobos) though to be captured asteroids.
Jupiter:Jupiter´s strong international heat creates a number of semi-permanent features in its atmosphere, such as cloud bands and the Great Red Spot. Jupiter has 63 known satellites.
Sturn:Saturn is distinguished by its extensive ring system, has several similarities to Jupiter, such as its atmospheric composition and magnetospere. The rings of Saturn are made up of small ice and rock particles . Saturn has 2 confirmed satellites; two which Titan and Enceladus, show signs of geological activity, though they are largely made of ice.

Uranus: Is the lightest of the outer planets. Uranus has 27 known satellites, the largest ones being Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel and Miranda.
Neptune: It radiatyesvmore international heat, but not as much as Jupiter orSaturn. Neptune has 13 known satellites. The largest, Triton, is geologically active, with geyers of liquid nitrogen.
Conclusion:
Force of gravity is verry important to keep everything in place including earth itself, these force of gravity keeps the others planets in the Solar Systeem in their porbits but mos of all prevents earth to fallin teh deep space.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)